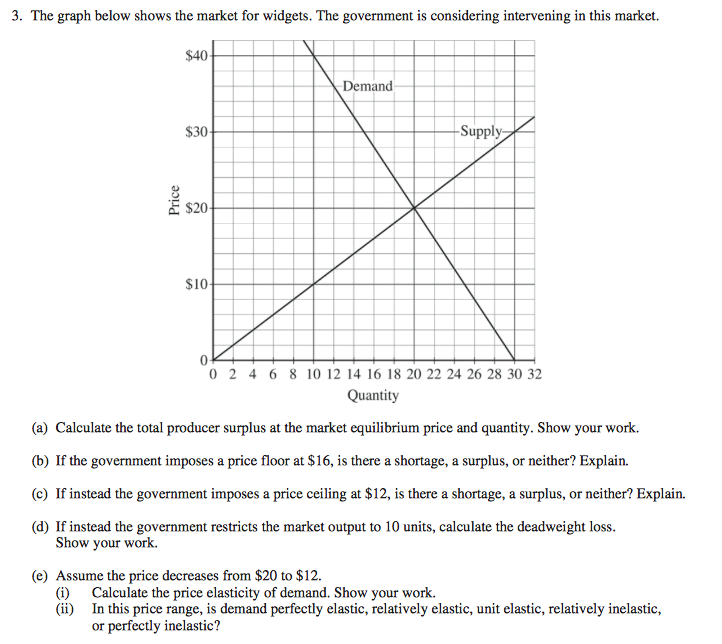
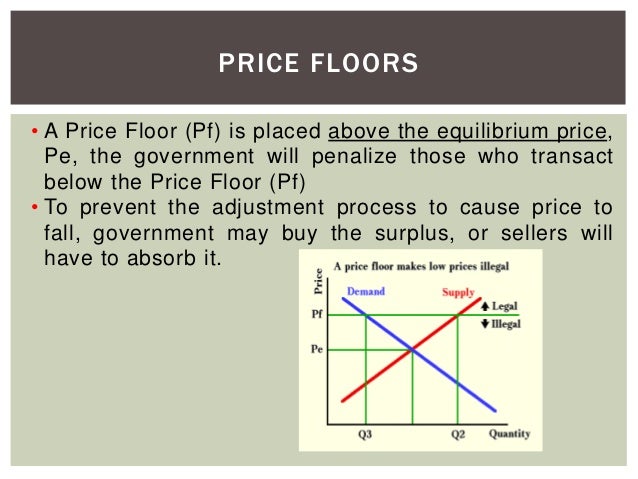
A Price Floor Is Usually Set The Equilibrium Price

A price floor example.
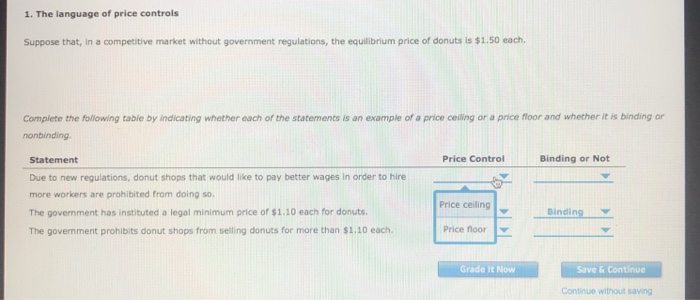
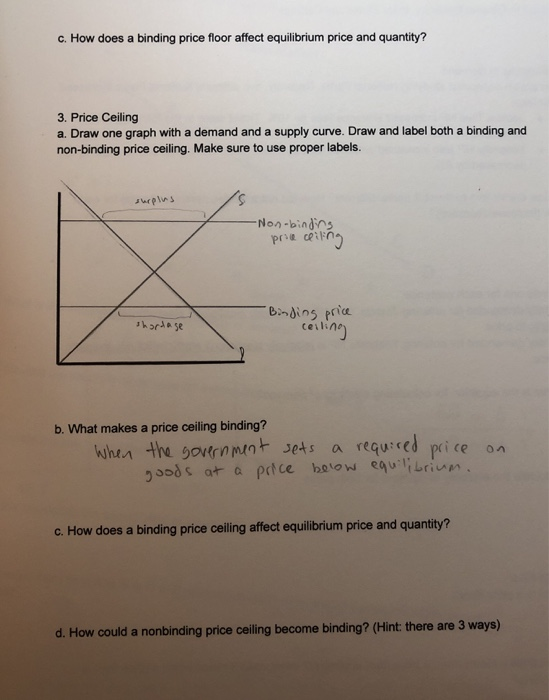
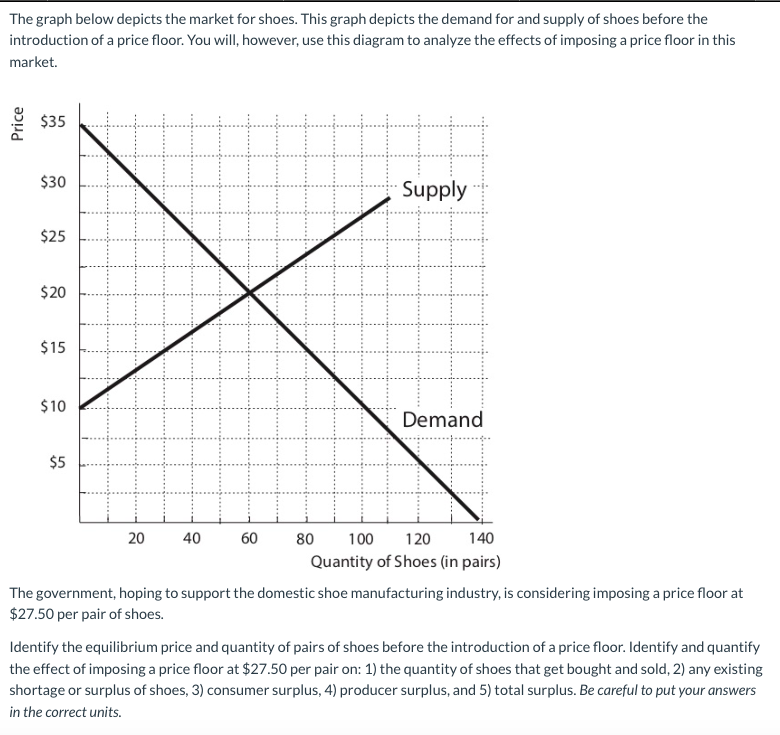
A price floor is usually set the equilibrium price. Price floors and price ceilings often lead to unintended consequences. Types of price floors 1. When a price floor is put in place the price of a good will likely be set above equilibrium. Simply draw a straight horizontal line at the price floor level.
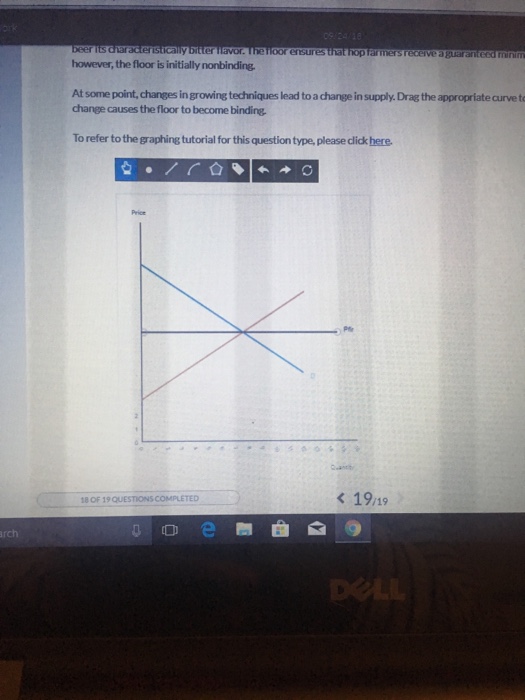
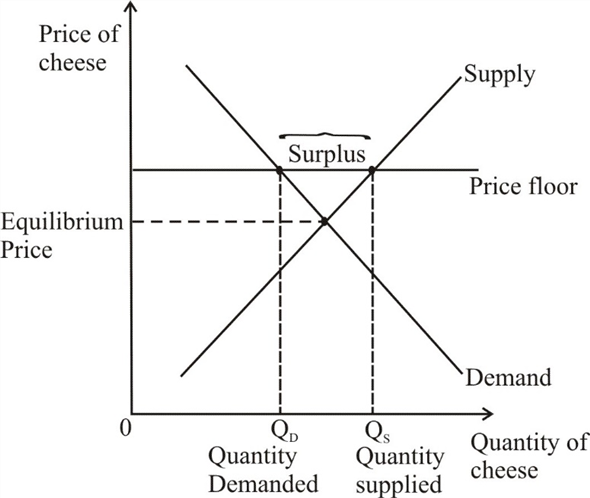
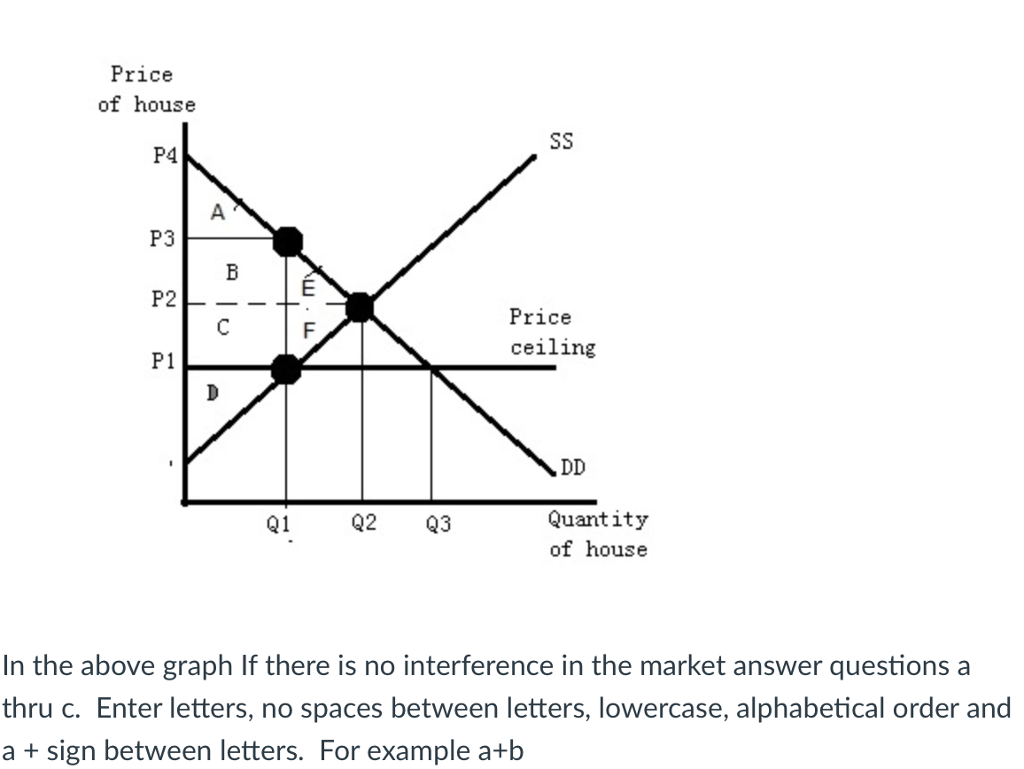
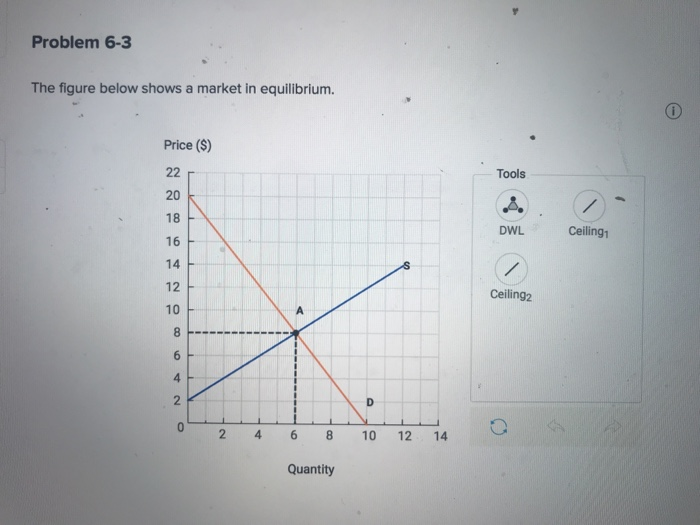
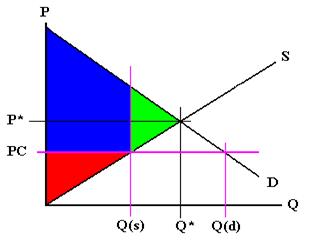
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level. If the price floor is low enough below the equilibrium price there are no effects because the same forces that tend to induce a price equal to the equilibrium price continue to operate. The intersection of demand d and supply s would be at the equilibrium point e 0. A binding price floor is a required price that is set above the equilibrium price.
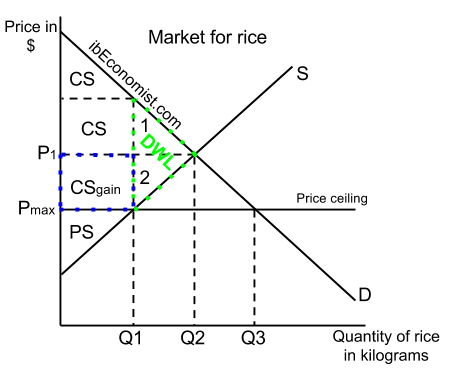
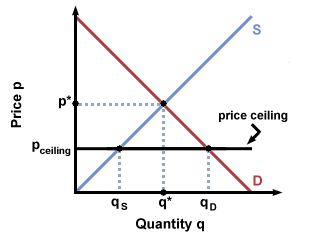
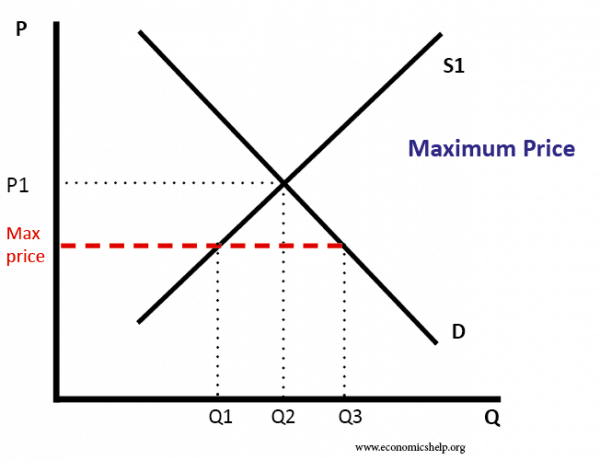
The government is inflating the price of the good for which they ve set a binding price floor which will cause at least some consumers to avoid paying that price. This has the effect of binding that good s market. The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external. A price ceiling is a type of price control usually government mandated that sets the maximum amount a seller can charge for a good or service.
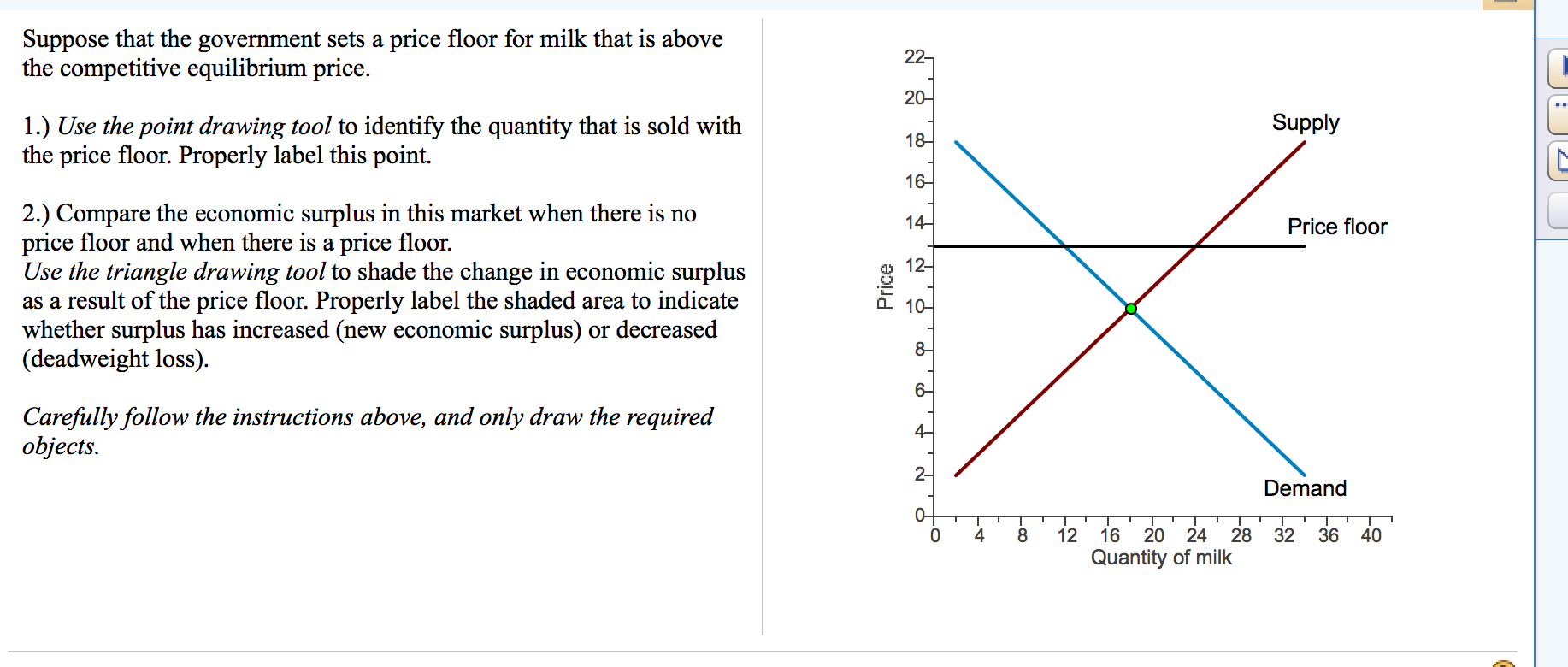
Governments usually set up a price floor in order to ensure that the market price of a commodity does not fall below a level that would threaten the financial existence of producers of the commodity. Only when the price floor is above the market equilibirum will in influence the market quantity and price. A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service. A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
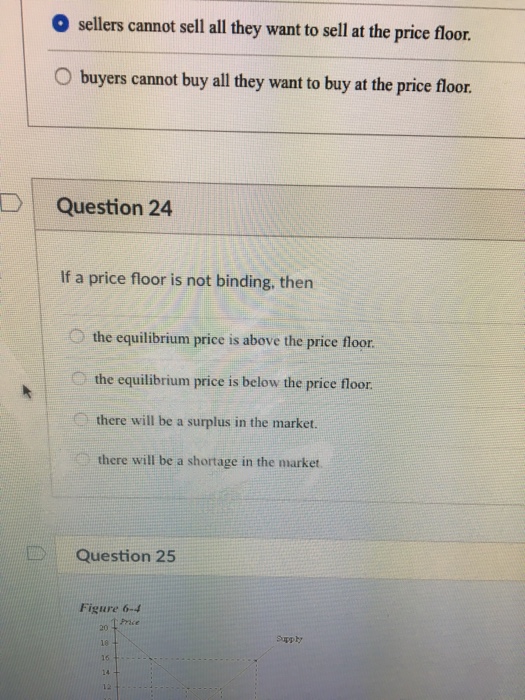
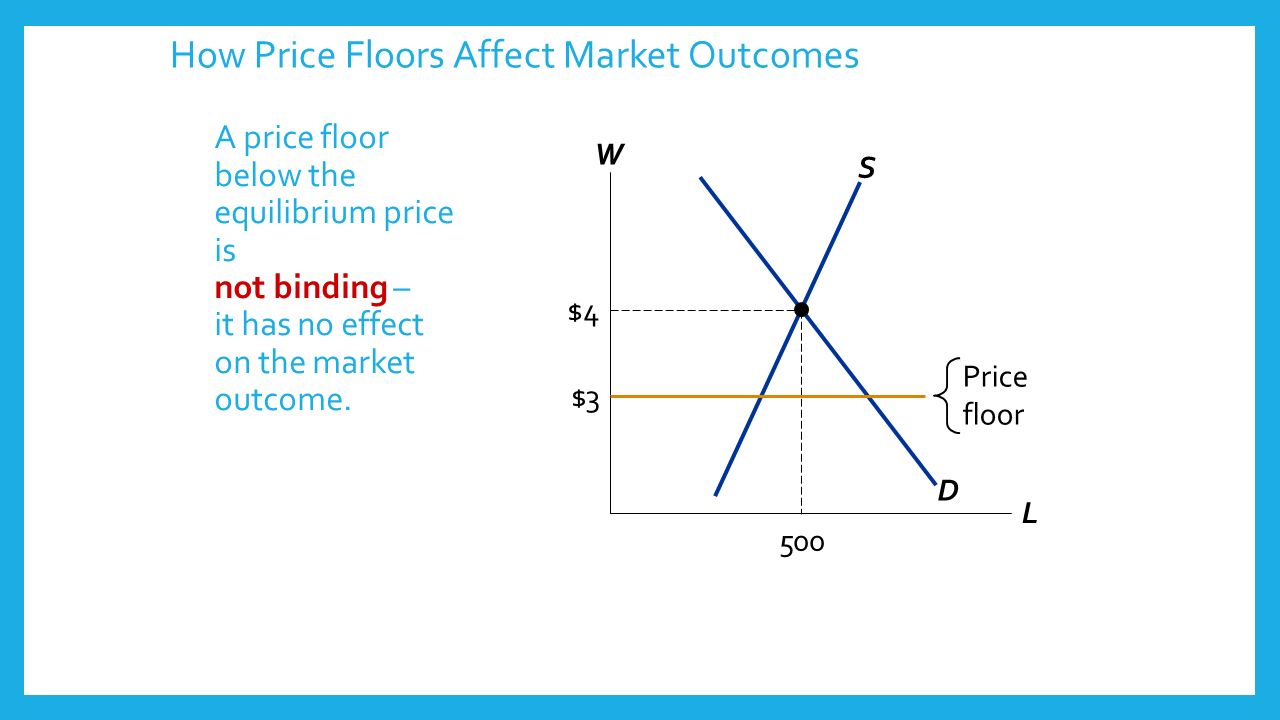
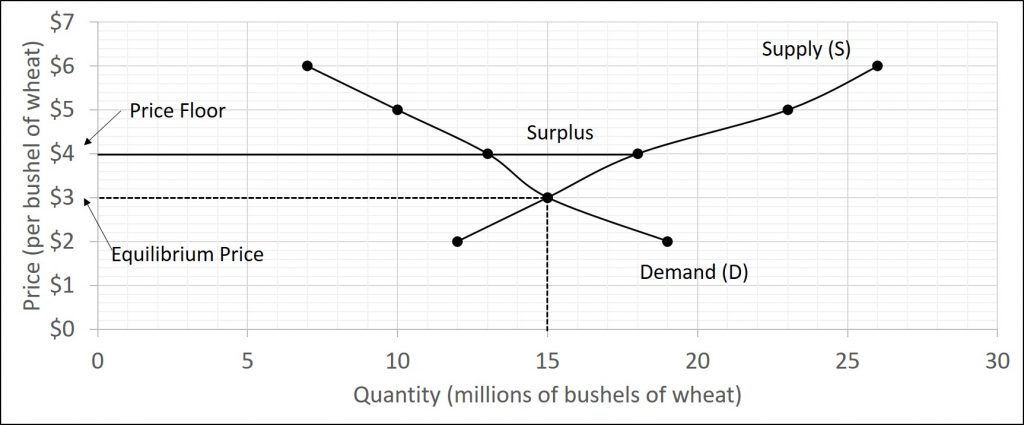
If the price floor is higher than the equilibrium price there will be a surplus because at the price floor more units are supplied than are demanded. If it s not above equilibrium then the market won t sell below equilibrium and the price floor will be irrelevant. When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded and excess supply or surpluses will result. When a price floor is set below the equilibrium price there is nothing preventing the price from rising to its equilibrium level.
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price as in this example it is considered a binding price floor. A price floor is an established lower boundary on the price of a commodity in the market. Drawing a price floor is simple.



















/disequilibrium-498e9ba4154c4a7c8739b3443da14b17.png)