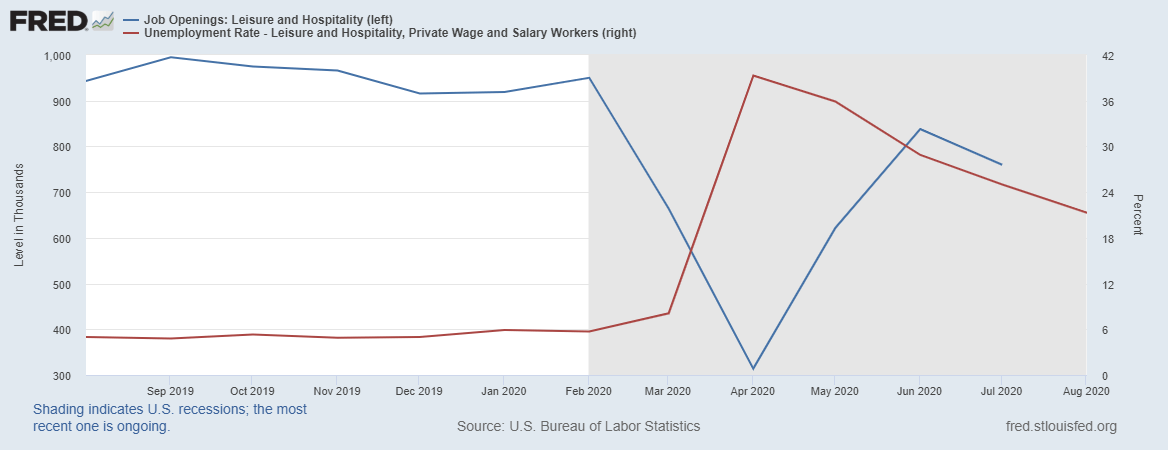
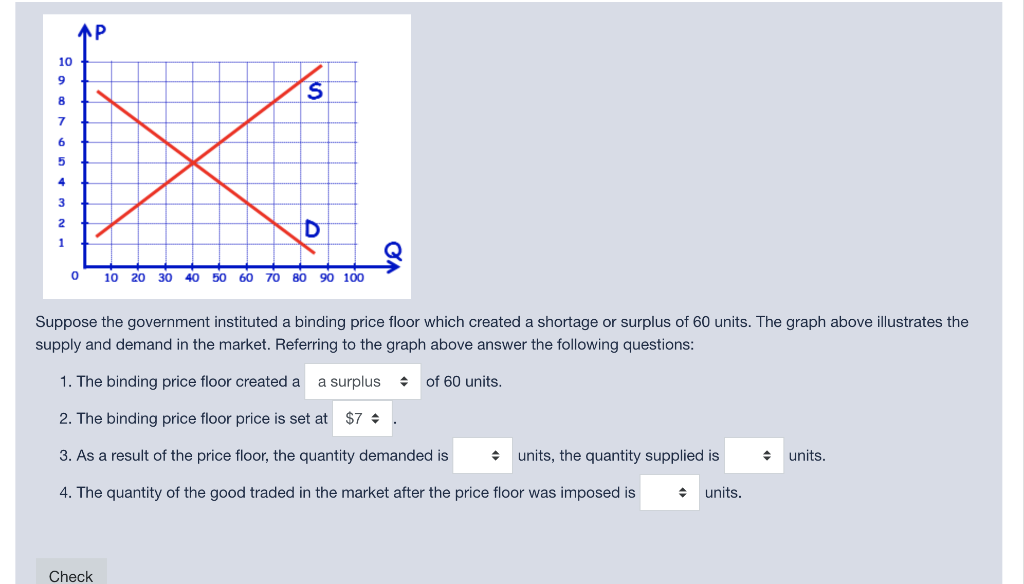
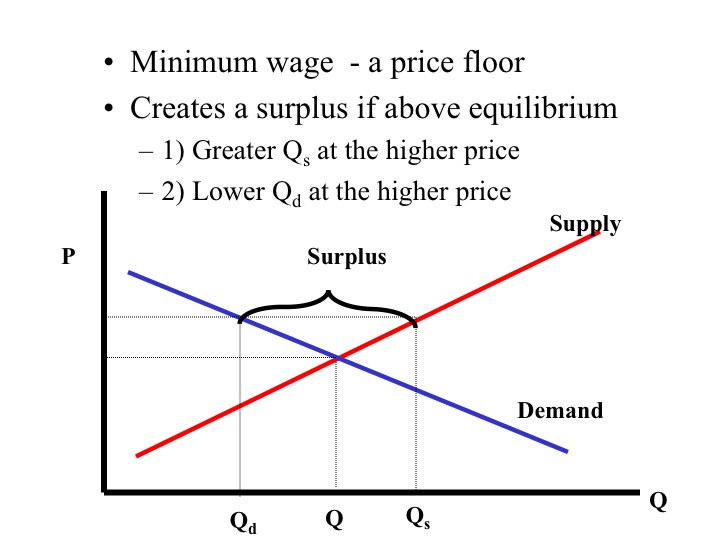
A Price Floor Set At 60 Would Create A Surplus Of 20 Units

A surplus of 100 units.
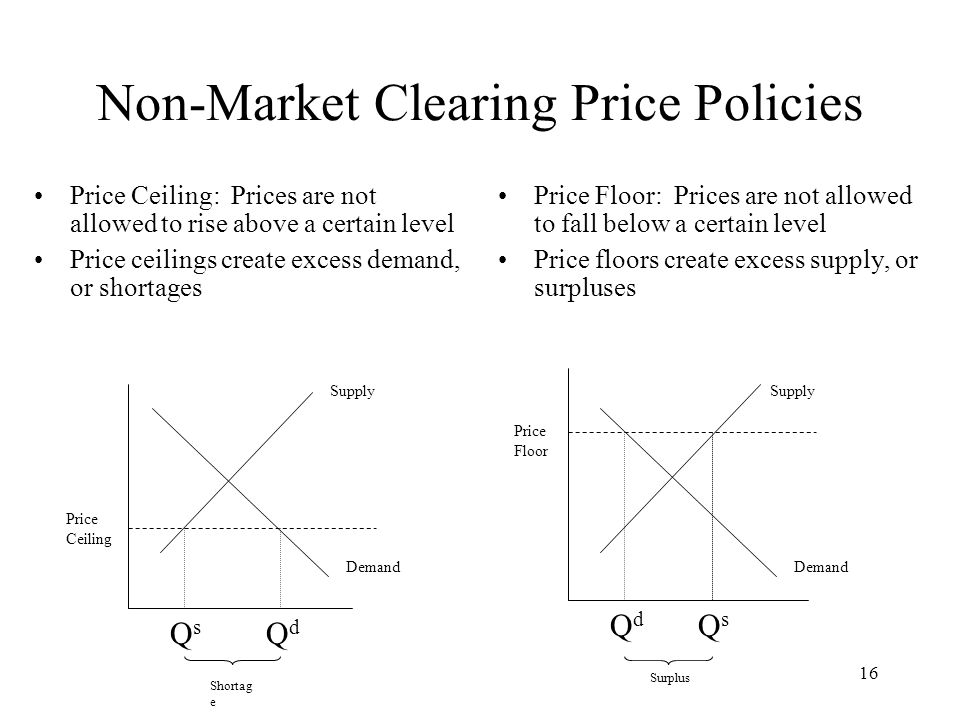
A price floor set at 60 would create a surplus of 20 units. The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied qs exceeds the quantity demanded qd. Create a price floor below which workers cannot. A shortage of 40 units. A price floor example.
A price floor set at 60 would create a surplus of 20 units true 5. A price floor set at 60 would create a surplus of 20 units. When the price of good a is 50 the quantity demanded of good a is 500 units. However a price floor set at pf holds the price above e 0 and prevents it from falling.
If the government imposes a price floor of 20 none of the above. When this economy produces 30 doghouses and 25 dishwashers there is full employment. Economists expect that a binding price floor will create a surplus in a market. D both answers a and c are correct.
A price floor set at 60 would create a surplus of 20 units. If a price floor of 5 was set the quantity sold would be 60 units. Refer to figure 6 26. A price floor set at 40 would create a surplus of 20 units.
A few crazy things start to happen when a price floor is set. 14 refer to figure 6 26. B is a type of price floor. A shortage of 20 units.
1 50 and an increase in price will result in a decrease in total revenue. C can create a surplus of labor. The minimum wage a is type of price ceiling. Surplus of 20 units b.
In the graph if a price floor on soybeans is set at 2 per bushel the amount of surplus in this market would be a. If a price floor of 5 was set. 15 for any given quantity the price on a demand curve represents the marginal buyer s willingness to pay. Simply draw a straight horizontal line at the price floor level.
D both answers a and c are correct. When the price of a good a rises to 70 the quantity demanded of good a falls to 400 units. Drawing a price floor is simple. When the price of good a rises to 70 the quantity demanded of good a falls to 400 units.
This graph shows a price floor at 3 00. A price floor of 60 results in. Using the midpoint method the price elasticity of demand for good a is a. A 4 000 b 2 000 c 3 000.
A shortage of 20 units d. When the price of good a is 50 the quantity demanded of good a is 500 units. Set at 800 how many apartment units are rented. 60 1 0 50 2 0 40 2 1 30 3 2 20 4 3.
Refer to the above figure. A surplus of 40 units c. False 0 icon koy figure 2 14 dates ibnd 30 s 60 refer to figure 2 14. The intersection of demand d and supply s would be at the equilibrium point e 0.
You ll notice that the price floor is above the equilibrium price which is 2 00 in this example. The tax rate ti tax revenue raised by the tax. First of all the price floor has raised the. Refer to the above figure.
















&cropxunits=300&cropyunits=168&width=580&height=385&mode=pad&bgcolor=333333&scale=both)